
Matter
- Elements (stœchī̂on)
- Fire (pŷr)
- Air (aḗr)
- Water (hýdōr)
- Earth (gē̂)
- Humors (chymós)
- Yellow Bile (xanthḕ cholḗ)
- Blood (hæ̂ma)
- Phlegm (phlégma)
- Black Bile (mélæna cholḗ)
- Bodies (sō̂ma)
- Organs (órganon)
Proper to the body only are change (e.g. of qualities), flux (e.g. of quantities), & separation (e.g. of substances).
The body (i.e. matter) exists as the concurrence of these qualities:
| Light | Heavy |
| Dense | Rare |
| Soft | Resistant |
| Fluid | Dry |
| Cold | Hot |
| Color | Shape |
| Outline | Extension |
| Note: |
It should be understood these are in themselves not matter but, rather, bare concepts.
Elements
| Element | Attributes |
|---|---|
| Fire | Hot & Dry |
| Air | Hot & Wet |
| Water | Cold & Wet |
| Earth | Cold & Dry |
Some class æther (æthḗr) as a fifth element (Latin: quintessence), while others consider it a special kind of fire. At any rate, it is celestial.
The elements & the sense each is the mean of:
| Element | Sense |
|---|---|
| Fire | Vision |
| Air | Hearing |
| Water | Smell |
| Earth | Taste |
The sense of touch is usually omitted as a common background sense.
Humors
| Humor | Organ |
|---|---|
| Yellow Bile | Gallbladder |
| Blood | Liver |
| Phlegm | Brain |
| Black Bile | Spleen |
Food is chewed through the mouth, passed down to the stomach, which then converts what is nutritious into a liquid & gives it to the liver, but sends what is not nutritious down to the intestine to be exited. The liver transforms the liquid from the stomach into like itself—i.e blood—& further sends the fiery impurities to the gallbladder, but the earthy impurities to the spleen. The liver then distributes the blood throughout the body via the veins. The kidneys catch the spent watery part of the blood, which acted as its vehicle along the veins & sends it down to the bladder to be exited.
Air is inhaled by the nostrils to the lungs, which hold it. The heart then takes the air from the lungs according to its rhythm, heats, & distributes breath throughout the body by the arteries. It also takes the expired breath from the arteries & sends it to the lungs to be exited. As the arteries contract with pulsation, the blood from the veins is drawn into the artery & infused with the breath, which is then sent back out into the veins with pulsation.
Organs
The senses & their organ of function:
| Sense | Organ |
|---|---|
| Vision | Eyes |
| Hearing | Ears |
| Smell | Nostrils |
| Taste | Tongue(s) |
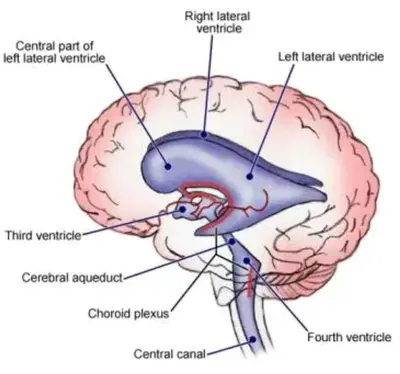
The soul’s faculties & their ventricle of function in the brain:
| Faculty | Ventricle |
|---|---|
| Imagination | Anterior |
| Reason | Interior |
| Memory | Posterior |
The divided senses are collected together in thet imagination, which in the rational creature then communicates the common sense by the reason to the intellect.
Soul
- Spirit (pneûma)
- Soul (psychḗ)
- Intelligent (logisticón)
- Incensive (thymoīdés)
- Appetitive (epithymēticón)
- Intellect (nûs)
- Reason (diánœa)
- Conception (epínœa)
- Sensations (ǽsthēsis)
- Vision (—)
- Hearing (—)
- Smell (—)
- Taste (—)
- Touch (—)
- Colors (chrō̂ma)
- White (leucû)
- Yellow (xanthòn)
- Red (phœnicûn)
- Purple (halurgón)
- Green (prásinon)
- Blue (cyanûn)
- Black (mélan)
The soul is the relation of body & spirit.
The will is a rational & vital force proper to the intellect.
Partitions
The partitions of the soul & each one’s local residence:
| Locale | Partition |
|---|---|
| Head | Intelligent |
| Chest | Incensive |
| Belly | Appetitive |
Faculties
The faculties of the soul & which are subject to reason:
| Condition | Faculties |
|---|---|
| Rational | Intellect |
| Memory | |
| Irrational | Imagination |
| Pulsative | |
| Seminal | |
| Generative | |
| Nutritive |
The pulsative principle is also called vital.
The seminal, generarive, & nutritive principles are also called the vegetable.
The faculties of the nutritive principle are: the attractive, the retentive, the transformative, & the excretive.
Colors
| Color | Hour |
|---|---|
| ⬜ White | ———— |
| 🟨 Yellow | Noonday |
| 🟥 Red | Afternoon |
| 🟪 Purple | Evening |
| 🟩 Green | Sunset |
| 🟦 Blue | Night |
| ⬛ Black | ———— |
White is the dilation of sight, but black is the contraction of it. Yellow, red, purple, green, & blue, are ratios of white & black.
Harmony
- Intervals (diástēma)
- Sound (phōnḗ)
- Point (mórion)
- Semitone (hēmitónio)
- Whole Tone (tónos)
- Fourth (diatessárōn)
- Fifth (diapénte)
- Tetrachord (tetráchordon)
- Octave (diapasō̂n)
- Unison (tautophōnía)
- Scales (gènos)
- Diatonic (diatonicó)
- Chromatic (chrōmaticó)
- Enharmonic (enarmónio)
- Modes (ḗchos)
- First (prō̂tos)
- Second (deúteros)
- Third (trítos)
- Fourth (tétartos)
- Plagal First (plágios tû prṓtu)
- Plagal Second (plágios tû deutéru)
- Grave (barýs)
- Plagal Fourth (plágios tû tetártu)
- Neumes (pneûma)
- Ison (íson)
- Oligon (olígon)
- Petasté (petastḗ)
- Centemata (centḗmata)
- Centema (céntēma)
- Hypselé (hypsēlḗ)
- Apsotrophe (apóstrophos)
- Hyporroé (hyporroḕ)
- Elaphron (elaphrón)
- Chamelé (chamēlḗ)
- Clasma (chlásma)
- Aplé (aplḗ)
- Diplé (diplḗ)
- Triplé (triplḗ)
Intervals
| Interval | Value/Ratio |
|---|---|
| Point | = 1 |
| Semitone | = 3 |
| Whole Tone | = 6 |
| Fourth | 4:3 |
| Fifth | 3:2 |
| Octave | 2:1 |
| Unison | 1:1 |
The octave is composed of a whole tone between two tetrachords, each tetrachord being composed of a fifth & a fourth.
Tones
| Chrysanthine |
|---|
| pa | bu | ga | di | ce | zō | nē |
From Chrysanthus of Mandytus (†7355 AM), following St. John Cucuzeles (†6869 AM), & SS. John of Damascus (†6258 AM) & Cosmo the Hymnographer (†6260 AM).
| Solfeggio |
|---|
| do | re | mi | fa | sol | la | si |
From Guido of Arezzo (†6542 AM), originally beginning with ut & ending with la, but Giovanni Battista Doni (7156 AM) changed the first syllable to do & added si.
The syllable do here corresponds to nē above.
Scales
| Diatonic | Soft Chromatic | Hard Chromatic | Enharmonic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pa | (—) | nē | (—) | pa | (—) | nē | (—) |
| bu | (12) | pa | (8) | bu | (6) | pa | (12) |
| ga | (10) | bu | (14) | ga | (20) | bu | (12) |
| di | (8) | ga | (8) | di | (4) | ga | (6) |
| ce | (12) | di | (12) | ce | (12) | di | (12) |
| zō | (12) | ce | (8) | zō' | (6) | ce | (12) |
| nē' | (10) | zō' | (14) | nē' | (20) | zō' | (12) |
| pa' | (8) | nē' | (8) | pa' | (4) | nē' | (6) |
| (Interval points from the prior.) |
Modes
| Mode | Scale | Tone |
|---|---|---|
| First | Diatonic | pa |
| Second | Soft Chromatic | di |
| Third | Enharmonic | ga |
| Fourth | Diatonic | bu, pa, di |
| Plagal First | Diatonic | pa, ce |
| Plagal Second | Hard Chromatic | pa |
| Grave | Enharmonic | ga, zō |
| Plagal Fourth | Diatonic | nē, ga |
The first four modes are, by some, called the authentic modes, with the last four called the plagal modes.
The modes are also, by some, called by the names of the ancient Greek modes:
| Mode | Greek Name |
|---|---|
| First | Dorian |
| Second | Phrygian |
| Third | Lydian |
| Fourth | Mixolydian |
| Plagal First | Hypodorian |
| Plagal Second | Hypophrygian |
| Grave | Hypolydian |
| Plagal Fourth | Hypomixolydian |
Neumes
Annotation
| Sign | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 𝁆 | Ison | Initial. |
| 𝁇 | Oligon | Ascend one. |
| 𝁉 | Petaste | Ascend one, stressed. |
| 𝁎 | Centemata | Ascend one, unstressed. |
| 𝁏 | Centema | Ascend two. |
| 𝁐 | Hypselé | Ascend four. |
| 𝁑 | Apostrophe | Descend one |
| 𝁓 | Hyporroé | Descend one then one. |
| 𝁕 | Elaphron | Descend two. |
| 𝁖 | Chamelé | Descend four. |
Duration
| Sign | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 𝀤 | Clasma | Adds one beat. |
| 𝂅 | Aplé | Adds one beat. |
| 𝂆 | Diplé | Adds two beats. |
| 𝂇 | Triplé | Adds three beats. |
Astronomy
- Heavens (uranō̂n)
- Firmament (steréōma)
- Stars (astḗr)
- Zodiac (zōdiacós)
- Ram (criós)
- Bull (taûros)
- Twins (dídymœ)
- Crab (carcínos)
- Virgin (parthénos)
- Scales (zygós)
- Scorpion (scorpíos)
- Archer (toxótēs)
- Capricorn (ægócerōs)
- Aquarius (hydrochóos)
- Fishes (ichthýes)
- Planets (planḗtēs)
- Saturn (crónos)
- Jupiter (zeús)
- Mars (árēs)
- Sun (hélios)
- Venus (aphrodítē)
- Mercury (hermē̂s)
- Moon (selḗnē)
- Temperaments (crásīs)
- Benefic (agathopœō̂n)
- Malefic (cacopœō̂n)
- Tropical (tropicón)
- Fixed (stereō̂n)
- Bicorporeal (disṓmatōn)
- Genders (génos)
- Masculine (arsnicō̂n)
- Feminine (thēlicō̂n)
- Sects (hǽresis)
- Diurnal (hēmerinō̂n)
- Nocturnal (nycterinō̂n)
- Aspects (schēmatismō̂n)
- Opposition (diámetron)
- Trine (trígōnœ)
- Quartile (tetrágōnœ)
- Sextile (hexágōnœ)
- Houses (œ́cōn)
- Age (æṓn)
- Time (chrónos)
- Critical Time (cærós)
- Year (étos)
- Seasons (epochḗ)
- Spring (ánœxis)
- Summer (théros)
- Autumn (phthinópōro)
- Winter (chīmṓn)
- Seasons (epochḗ)
- Months (mḗn)
- Nights (nýx)
- Days (hēméra)
- Hours (hṓra)
A star is oriental when rising & setting ahead of the sun, but occidental if following the sun.
Heavens
| Sphere | Revolution |
|---|---|
| Stars | → |
| Saturn | ← |
| Jupiter | |
| Mars | |
| Sun | |
| Venus | |
| Mercury | |
| Moon | |
| (Æther) | |
| Fire | ↑ |
| Air | |
| Water | ↓ |
| Earth |
The sphere of stars is called the firmament. That of the planets, the heavens. That of the elements, the earth. Each sphere of the heavens is itself called a heaven. The collection of all the spheres beyond that of water is sometimes also called the heavens, taken as a set of three: the spheres of air & fire, taken together as the first; all seven of the planets, the second; & the firmament, the third.
Some conceive the world as semi-concentric spheres moved around each other, where east & west, north & south, are intersecting circles. Some conceive the world as semicircles instead, where east & west circle around north, but south, the extremity from the center. Christians say either view is acceptable, but the gentiles only accept the former view. At any rate, each planet is moved in an additional sphere of its own within its respective sphere or semicircle.
Stars
All the ancients were in harmony regarding the number of constellations: forty eight. No more nor less. There was disagreement regarding what those were, but not how many.
The Ægyptians called the thirty six non-zodiac constellations decans because each marked the passage of ten days. They then divided the constellations into twelve groups of four—one zodiac with three decans. An additional five—now five & a quarter—days were added for a total of three hundred & sixty five days in the year. Thus, the decans told the days, & the zodia, the months. In the span of these days, whatever zodiac sign the sun enters at the beginning, e.g. the ram, it will enter it again at the end.
The Persians distinguished a constellation called the bands from the fishes, & did not recognize the horse. Some Greeks did not distinguish the scales from the scorpion.
Zodia
| Sign | Name | Temperament | Gender | Sect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♈︎ | Ram | Equinoctial | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♉︎ | Bull | Fixed | Feminine | Nocturnal |
| ♊︎ | Twins | Bicorporeal | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♋︎ | Crab | Tropical | Feminine | Nocturnal |
| ♌︎ | Lion | Fixed | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♍︎ | Virgin | Bicorporeal | Feminine | Nocturnal |
| ♎︎ | Scales | Equinoctial | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♏︎ | Scorpion | Fixed | Feminine | Nocturnal |
| ♐︎ | Archer | Bicorporeal | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♑︎ | Capricorn | Tropical | Feminine | Nocturnal |
| ♒︎ | Aquarius | Fixed | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♓︎ | Fishes | Bicorporeal | Feminine | Nocturnal |
| Note |
|---|
| Each of the twelve zodia has thirty degrees, ten for each decan, thus totaling three hundred & sixty. Man, correspondingly, has two sets of twelve ribs, & three hundred & sixty joints. |
Aspects
| Zodiac | Commands | Obeys | Beholds |
|---|---|---|---|
| ♈︎ | – | – | ♎︎ |
| ♉︎ | ♓︎ | – | ♍︎ |
| ♊︎ | ♒︎ | – | ♌︎ |
| ♋︎ | ♑︎ | – | – |
| ♌︎ | ♐︎ | – | ♊︎ |
| ♍︎ | ♏︎ | – | ♉︎ |
| ♎︎ | – | – | ♈︎ |
| ♏︎ | – | ♍︎ | ♓︎ |
| ♐︎ | – | ♌︎ | – |
| ♑︎ | – | ♋︎ | ♒︎ |
| ♒︎ | – | ♊︎ | ♑︎ |
| ♓︎ | – | ♉︎ | ♏︎ |
Triplicities
| Zodia | 🜚 Governor | ☾ Governor | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| ♈︎ ♌︎ ♐︎ | 🜚 ♃ | id. | N-W |
| ♉︎ ♍︎ ♑︎ | ♀ | ☾ | S-E |
| ♊︎ ♎︎ ♒︎ | ♄ | ☿ | N-E |
| ♋︎ ♏︎ ♓︎ | ♂ | ♀ | S-W |
Months
| Zodiac | Month | Days | 🜚 Entry |
|---|---|---|---|
| ♈︎ | March | 31 | 21 |
| ♉︎ | April | 30 | 23 |
| ♊︎ | May | 31 | 23 |
| ♋︎ | June | 30 | 24 |
| ♌︎ | July | 31 | 25 |
| ♍︎ | August | 31 | 25 |
| ♎︎ | September | 30 | 25 |
| ♏︎ | October | 31 | 25 |
| ♐︎ | November | 30 | 25 |
| ♑︎ | December | 31 | 25 |
| ♒︎ | January | 31 | 25 |
| ♓︎ | February | 28 | 24 |
Although the months are evidently based on the zodia, this exact order of names originates from Romulus (4793 AM), at first being only ten months (March to December). Numa Pompilius (4837 AM), the second king of Rome, then added the other two. All of these had less days, & so intercalary months were inserted. Julius Cæsar added the days as we now have, & ceased the insertion of intercalary months, rather having February 24th doubled every four years.
According to Christians, the Archangel Uriel revealed the solar year to Enoch (†1487 AM), & he thence taught it to his descendents. But according to the gentiles, Zoroaster (3897 AM) discovered it.
See the Syrian page for the ancient Assyrian month names.
Seasons
| Zodiac | Season | Quality |
|---|---|---|
| ♈︎ | Spring | Wet |
| ♋︎ | Summer | Hot |
| ♎︎ | Autumn | Dry |
| ♑︎ | Winter | Cold |
Each season begins at the solar entry of its respective zodiac (see above).
Planets
| Sign | Name | Temperament | Gender | Sect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♄ | Saturn | Malefic | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♃ | Jupiter | Benefic | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♂ | Mars | Malefic | Masculine | Nocturnal |
| 🜚 | Sun | Common | Masculine | Diurnal |
| ♀ | Venus | Benefic | Feminine | Nocturnal |
| ☿ | Mercury | Common | Common | Common |
| ☾ | Moon | Benefic | Feminine | Nocturnal |
Mercury is malefic, male, & diurnal if oriental, but benefic, female, & nocturnal if occidental.
The tokens for each are from Roman astronomy: Saturn’s & Jupiter’s are stylized initials—κρ & ζε, respectively—Mars’ is a spear & shield, Venus’, a hand-mirror, Mercury’s, a caduceus, the Sun’s & the Moon’s, a solar beam & lunar crescent respectively.
Crosses were added to the planetary symbols sometime in the 71st century AM.
Before the planets were named after the gentile gods, they were called:
| Planet | Ancient Name |
|---|---|
| ♄ | Shining (phǽnōn) |
| ♃ | Radiant (phaéthōn) |
| ♂ | Fiery (pyóīs) |
| ♀ | Evening (hésperos) |
| Morning (phōsphóros) | |
| ☿ | Twinkling (stílbōn) |
Houses
| Planet | 🜚 House | ☾ House | Exaltation | Depression |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♄ | ♑︎ | ♒︎ | ♎︎ | ♈︎ |
| ♃ | ♐︎ | ♓︎ | ♋︎ | ♑︎ |
| ♂ | ♏︎ | ♈︎ | ♑︎ | ♋︎ |
| 🜚 | ♌︎ | – | ♈︎ | ♎︎ |
| ♀ | ♎︎ | ♉︎ | ♓︎ | ♍︎ |
| ☿ | ♍︎ | ♊︎ | ♍︎ | ♓︎ |
| ☾ | – | ♋︎ | ♉︎ | ♏︎ |
Hours
| Weekday | j. | ij. | iij. | iv. | v. | vj. | vij. | viij. | ix. | x. | xj. | xij. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ |
| ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | |
| Second | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 |
| ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | |
| Third | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ |
| ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | |
| Fourth | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ |
| 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | |
| Fifth | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ |
| ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | |
| Sixth | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ |
| ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | |
| Seventh | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ |
| ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ | 🜚 | ♀ | ☿ | ☾ | ♄ | ♃ | ♂ |
Each hour from evening is associated with a planet, cycling through them all then in seven hours, so that the day is associated with the planet of its first hour.
However, Christians & the gentiles do not call the weekdays by the same names:
| Weekday | Christian Name | Gentile Name |
|---|---|---|
| First | Lord’s (cyriacḕ) | Sunday (hēlíu) |
| Second | Second (deutéra) | Monday (selḗnēs) |
| Third | Third (trítē) | Tuesday (áreōs) |
| Fourth | Fourth (tetártē) | Wednesday (hermû) |
| Fifth | Fifth (pémptē) | Thursday (diós) |
| Sixth | Preparation (parasceuḕ) | Friday (aphrodítēs) |
| Seventh | Sabbath (sábbaton) | Saturday (crónu) |
Constellations
Northern Ecliptic
| Constellation | Count |
|---|---|
| Lesser Bear | (7—1) |
| Greater Bear | (27—8) |
| Dragon | (31) |
| Cepheus | (11—2) |
| Plowman | (22—1) |
| Northern Crown | (8) |
| Hercules | (17—1) |
| Lyre | (10) |
| Bird | (17—2) |
| Cassiopia | (13) |
| Perseus | (266—3) |
| Charioteer | (14) |
| Serpentarius | (24—5) |
| Serpent | (18) |
| Arrow | (5) |
| Eagle | (9—6) |
| Dolphin | (10) |
| Foal | (4) |
| Horse | (20) |
| Andromeda | (23) |
| Triangle | (4) |
Northern Zodia
| Constellation | Count |
|---|---|
| Ram | (13—5) |
| Bull | (33—11) |
| Twins | (18—7) |
| Crab | (9—4) |
| Lion | (27—5) |
| Virgin | (26—6) |
Southern Zodia
| Constellation | Count |
|---|---|
| Scales | (8—9) |
| Scorpion | (21—3) |
| Archer | (31) |
| Capricorn | (28) |
| Aquarius | (42—3) |
| Fishes | (34—4) |
Southern Ecliptic
| Constellation | Count |
|---|---|
| Cetus | (22) |
| Orion | (38) |
| River | (34) |
| Hare | (12) |
| Dog | (18—11) |
| Antecanis | (2) |
| Argus | (45) |
| Hydra | (25—2) |
| Bowl | (7) |
| Raven | (7) |
| Centaur | (37) |
| Wild-beast | (19) |
| Censer | (7) |
| Southern Crown | (13) |
| Southern Fish | (12—6) |
The first number is the count of stars in the constellation, the second, the count of unshaped stars, i.e., those not part of a constellation.
Many so-called constellations that are contemporaneously known are parts of these, e.g. the so-called southern cross is really the centaur’s right hind leg.
Other
Measurements
- Lengths
- Digit (dáctylos)
- Palm (palæstḗ)
- Span (spithamḗ)
- Foot (pûs)
- Cubit (pē̂chys)
- Pace (bē̂ma)
- Fathom (orgyiá)
- Perch (decápodon)
- Plethron (pléthron)
- Stade (stádion)
- Mile (mílion)
- Area
- Acre (strémma)
- Weights
- Scruple (grámma)
- Semis (sēmmísis)
- Solidus (nómisma)
- Ounce (ungía)
- Pound (lítra)
- Volumes
- Cup (cotýlē)
- Pot (xéstēs)
- Handful (phûcta)
λͅ & £ are abbreviation signs for pound, Greek lítra & Latin libra. The latter is only used contemporarily for British money.
The foot was standardized by that of Agrippa—general of Emperor Augustus, & husband of his daughter Julia the Elder—when he built what would become the Church of the Mother of God & the Martyrs, Italy.
Lengths
| Measure | Definition | Equals (ft.) | Equals (dig.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digit | = 1 digit | = 1/16 ft. | = 1 dig. |
| Palm | = 4 digits | = 1/4 ft. | = 4 dig. |
| Span | = 3 palms | = 3/4 ft. | = 12 dig. |
| Foot | = 4 palms | = 1 ft. | = 16 dig. |
| Cubit | = 2 spans | = 1 1/2 ft. | = 24 dig. |
| Pace | = 2 1/2 feet | = 2 1/2 ft. | = 40 dig. |
| Double Pace | = 5 feet | = 5 ft. | = 80 dig. |
| Fathom | = 8 spans | = 6 ft. | = 96 dig. |
| Perch | = 10 feet | = 10 ft. | = 160 dig. |
| Plethron | = 10 perches | = 100 ft. | = 1,600 dig. |
| Stade | = 6 plethra | = 600 ft | = 9,600 dig. |
| Mile | = 8 1/3 stadia | = 5,000 ft. | = 80,000 dig. |
| Day’s Journey | = 3 miles | = 150,000 ft. | —————— |
| Week’s Journey | = 21 miles | = 1,050,000 ft. | —————— |
- The digit is also called the finger & unit.
- The palm is also called the handbreadth.
- The perch is also called the rod.
- The stade is now called the cable.
- The French meter is equal to 3.28 ft.
Conversion of contemporary lengths:
| Measure | Definition | Equals (ft.) | Equals (dig.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inch | = 1/12 foot | = 1/12 ft. | = 1 1/2 dig. |
| Yard | = 1/2 fathom | = 3 ft. | = 48 dig. |
| Furlong | = 1 stade | = 600 ft. | = 9,600 dig. |
| League | = 1 1/2 miles | = 7,500 ft. | = 120,000 dig. |
Area
| Measure | Definition | Equals (ft.) |
|---|---|---|
| Acre | = 1×1 plethron | = 100×100 ft. |
Weights
| Measure | Definition | Equals (lb.) |
|---|---|---|
| Scruple | = 1/24 ounce | = 3/64 lb. |
| Semis | = 1/12 ounce | = 5/64 lb. |
| Solidus | = 1/6 ounce | = 1/72 lb. |
| Ounce | = 1 ounce | = 1/12 lb. |
| Pound | = 12 ounces | = 1 lb. |
Conversion of contemporary weights:
| Measure | Definition | Equals (lb.) |
|---|---|---|
| Carat | = 1/144 ounce | = 1/1,728 lb. |
| Obole | = 1/48 ounce | = 1/64 lb. |
Volumes
| Measure | Definition | Equals (lb.) |
|---|---|---|
| Ounce | = 1 ounce | = 1/12 lb. |
| Cup | = 1 1/2 ounces | = 1/8 lb. |
| Pot | = 3 ounces | = 1/4 lb. |
| Pound | = 12 ounces | = 1 lb. |
| Handful | = 18 1/2 ounces | = 1 13/34 lbs. |
Conversion of contemporary volumes:
| Measure | Definition | Equals (oz.) |
|---|---|---|
| Pint | = 1/2 quart | = 2 1/4 oz. |
| Quart | = 1/4 gallon | = 4 1/2 oz. |
| Gallon | = 6 pots | = 18 oz. |
References
- John of Damascus, St. “An Exact Exposition of the Orthodox Faith” in: The Fount of Knowledge.
Nature
- Nemesius of Emesa. On the Nature of Man.
- Galen. On the Faculties of Aliments.
- Galen. On the Natural Faculties.
- Galen. On the Usefulness of Parts.
- Hippocrates. Humors.
- Plato. Timæus.
- Iamblichus. The Theology of Arithmetic.
- Pliny the Elder. Natural History
Harmony
- Aristoxenus. Harmonics
- Nicomachus. Manual of Harmonics.
- Ptolemy, Claudius. Harmonics.
Astronomy
- Ptolemy, Claudius. Tetrabiblos.
- Ptolemy, Claudius. Almagest.
- Aristotle. Meteorology.